10mm Thickness for Passivhaus-Level Performance: Why Aerogel Blanket Replaced Rockwool & VIP in 2025 Real Projects – Case Studies & Insights
Published: 2025-02-28
| Updated: 2026-02-06
Aerogel Insulation Solutions
Space is premium in retrofits and high-density builds. Hydrophobic aerogel blankets (λ ≈ 0.020 W/(m·K), A1-rated, >99% water-repellent) achieve superior U-values with minimal thickness, outperforming rockwool (bulkier, higher λ) and VIP (brittle, costly). Explore 4 real 2025 cases from Australia and China: 70% thickness reduction, 68% heating savings, condensation elimination, and +5% sellable area. Includes specs, best practices, and pricing from Hebei Woqin Trading Co., Ltd.
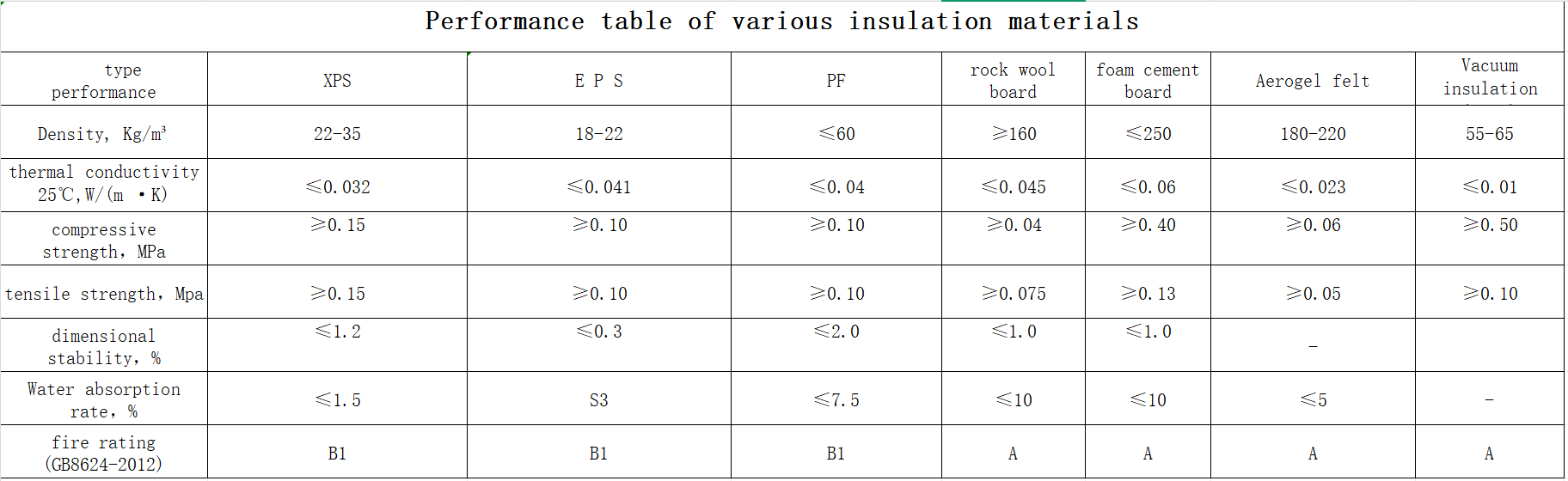
In high-performance building projects—Passivhaus, EnerPHit, Green-Star-3—architects and developers constantly battle thickness constraints, thermal bridges, condensation, and lost floor area. Traditional rockwool (λ ≈ 0.035–0.045 W/(m·K)) demands 100+ mm, PIR/XPS similar bulk, while VIP (0.002–0.005 W/(m·K)) offers thinness but risks puncture and high cost for large areas.
Aerogel blanket is distinct: flexible, hydrophobic silica aerogel composite (A1/A2 non-combustible, 99.7% hydrophobicity per GB/T 10299-2011), with real-world thermal conductivity 0.020 W/(m·K) at 25°C (GB/T 10295-2008). It delivers near-VIP efficiency in 3–20 mm layers, without brittleness, and crushes rockwool on space and moisture resistance.
In 2025 projects we've supported across Australia and China, aerogel blanket replaced thicker alternatives, delivering measurable wins. Here are four standout examples:
Case 1: Fitzroy, Melbourne – 1890s Double-Brick Heritage Terrace (EnerPHit Certified Jan 2025)
Original: 100 mm rockwool external.Switched to: 10 mm hydrophobic aerogel blanket.+50 mm ventilated rainscreen.
Result: Final wall U-value 0.30 W/(m²·K) (including bridges); added thickness only 58 mm. Heritage facade preserved while meeting EnerPHit standards—no major structural rework.
Case 2: Mosman, Sydney – Coastal Light Steel Frame House
Original: 120 mm rockwool in studs.
Switched to: 10 mm aerogel blanket fully wrapped.
Result: Steel stud bridge penalty dropped from 0.38 to 0.07 W/(m²·K); heating bill reduced 68% last winter. Minimal interior space loss in high-value coastal site.
Case 3: Lujiazui, Shanghai – Green-Star-3 Office Tower Curtain Wall
Issue: Aluminium mullion cold bridges (surface temp 11°C, condensation risk).
Solution: 5 mm adhesive-backed aerogel blanket, wrapped on mullions.
Result: Coldest surface rose to 18.1°C; zero condensation. Client expanded scope to three additional towers.
Case 4: Nanshan, Shenzhen – 18-Storey Affordable Housing
Original tender: 100 mm rockwool + 50 mm XPS.
Switched to: 10 mm aerogel blanket+ 30 mm pearl mortar.
Result: Insulation thickness cut by 70 mm; developer gained ~5% extra sellable floor area (estimated +100 million RMB profit). Energy codes met with slimmer envelope.
These results come from aerogel's nanoporous structure: high surface area traps still air, suppresses conduction/convection/radiation. Third-party tests (e.g., GB/T 34336-2017) confirm:
• Vibration mass loss: 0.3% (≤1.0%).
• Tensile strength: Transverse 1255 kPa, longitudinal 414 kPa.
• Fire: A1 non-combustible (combustion heat 1.9 MJ/kg ≤2.0, furnace rise 2°C ≤30, sustained burning 0 s).
• Hydrophobicity: 99.7%.
Our 2025 Stock Models
• Thickness: 3/5/10/20 mm hydrophobic A1/A2 aerogel blanket.
• Options: With/without PE film or aluminium foil vapour barrier.
• Roll: 1.5 m width, customizable length.
Installation Best Practices (Site-Proven)
• Substrate: Clean, dry surface—adhesive fails on dust/oil in days.
• Joints: 45° scarf joints at corners (avoid butt joints).
• Fixings: Screws through rainscreen battens need insulation washers.
• Cutting: Hot knife only—no dust from utility knives.
• Orientation: Follow roll "grain" for conformability.
2025 Landed Pricing (40HQ Reference)
• 6 mm A1: ≈ US$38–42/m²
• 10 mm A1: ≈ US$52–58/m²
2026 forecast:
20–25% reduction as new production lines scale (market trends show aerogel capacity expanding rapidly).
Limitations & When to Choose Alternatives
Aerogel blanket excels in non-load-bearing envelopes with strict thickness/humidity/fire requirements (walls, curtain walls, steel wraps, heritage retrofits). It is not ideal for extreme mechanical loads or prolonged immersion—pair with rigid materials like foamed glass for loaded flat roofs.
Full Technical Package Available
Request our free folder: PHPP files, 25-year Nordic ageing reports, CAD details, infrared photos, heat-flux data, full third-party reports (including EU rep: TOCYA TRADING, Paris, valid to Sep 2026).
Contact: Ruibin An
Hebei Woqin Trading Co., Ltd.
Phone/WhatsApp/WeChat: +86 139 3392 9092
Email: an@cn-aerogel.com
In net-zero buildings, thin reliable insulation drives ROI. Aerogel blanket proves it—where space, performance, and sustainability intersect. Let's discuss your project needs.

Written by - Ruibin An
Founder & Managing Director
Industry Veteran with 13+ Years of Experience. Deeply rooted in the insulation industry for over 13 years, specializing in supply chain optimization and global market trends for Rock Wool and Aerogel materials.
Related Insulation Solutions
LATEST NEWS
Don't Be Fooled by Reflective Paints: Why Your Industrial Roof Gets Hot Again in Year Two
2026-02-19
Stop the Bulk: How to Choose the Right "Core" for Removable Insulation Jackets? (Aerogel vs. Rockwool Real-World Comparison)
2026-02-16
The "Great Squeeze" of 2026: Why Your 90-Day Terms Are Putting 25-Year Assets at Risk
2026-02-14
Closing the 0.005 W/mK Gap: How EV Battery Tech Solved a Passive House Thermal Bridge Nightmare
2026-02-12
The 98% UK Retrofit Failure: The Vapor-Open Aerogel Fix (μ<5)
2026-02-09

